Depends upon the type of extrusion process, we need to consider many factors which will make metal extrusion process very economical for both small and large scale batch production. Size of billet, material type, required cross section of extruded component, speed of the ram which pushes billet through die, working temperature and type of metal extrusion process, are all significant elements in your design consideration and optimization of an extrusion operation. The main objective is to get the right metal flow with the optimum force requirement from ram. The force is applied through a ram is supplied mostly by hydraulic press. Most extrusions are performed horizontally by hydraulic presses which can move the ram at a constant speed, also maintaining constant force over a long stroke. This makes hydraulic press suitable for extruding metal components.
Ram Speed
The ram’s speed affects the forces involved during the operation. Ram can be made to move as low as a few meter per minute, or move as high as 4.6 meter per second, though best practice is 0.6 meter per second. The Most common length of extruded metal product in practice is usually up to 7.6 meter, but longer lengths as high as 27.5 meter also possible in extrusion process. Most of the extruded components produced through extrusion machines require post-processing operation like bending or straightening after the completion of the extrusion process.
Metal Flow during Extrusion
Imagine the flow of metal trough the die similar to water flowing through the reducer of smaller width. In extrusion process, metal from the billet of round cross section forced to flow through the much little cross-section area of die. The material gets deformed as it travels through the die, the outermost layers close to the die surface experiences much greater material displacement than layers around the central axis. The turbulent flow of material happens at outer layer and material around central axis moves faster in high velocity compared to outer layer.
If you use square die of 90deg angle, layers close to the die won’t move and results in stagnation of metal flow called dead metal zone. So extrusion die angle plays an important role in extrusion process.
Extrusion Die Angle
Next important factor in extrusion process is Extrusion die angle as it is the contributing factor in the flow of material. The amount of force to extrude to form a reduced cross section will depends on die angles.
Friction is a culprit that increases the required force to extrude a part. A low angle die will create more friction at the work-die meet up point which is not good. If you thinking of to have maximum die angles, We don’t recommend it. It is because more anlge allows more material movement inthe outer layers which create turbulence in the metal flow. If turbulence is more, then force required will be more.
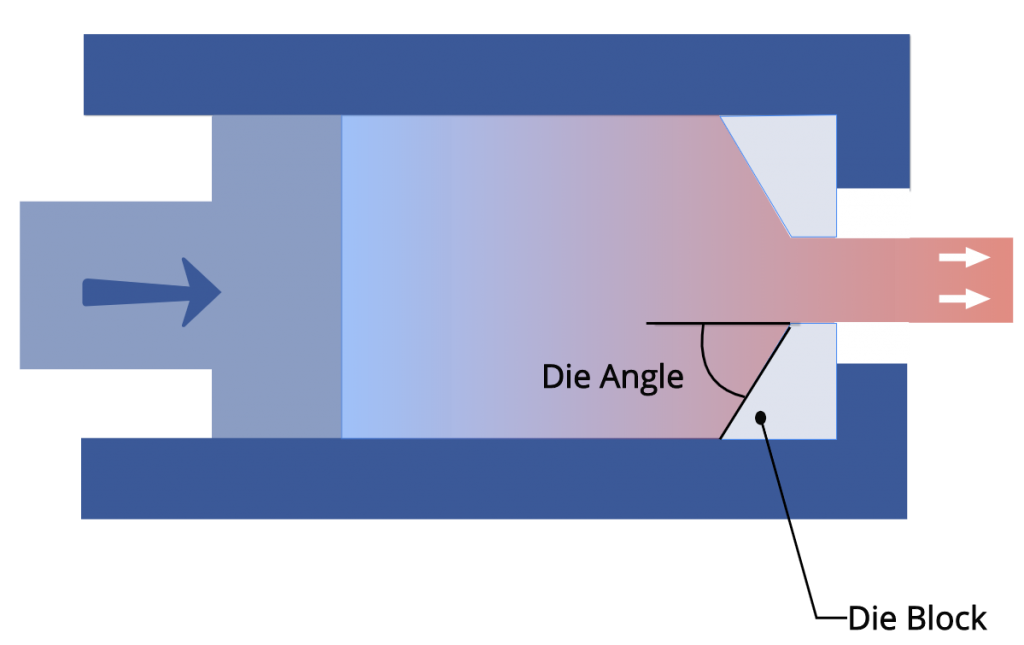
We should make a deal where everyone is not very happy. Having optimum die angle to reduce friction, also less turbulence would be ideal. How to calculate the die angle? To arrive optimum die angle is difficult, based on all the feedback of a collected during operation, engineer must try to provide the optimum angle
Extrusion Ratio
As we explained earlier. during extrusion process is large amount of metal deformation of the material will happen. The cross section of the billet is larger than the cross section of the extruded component. In below example, billet which is 20mm diameter is deformed into extrusion with a diameter of 10mm. This round cross-section is simple to relate in terms for reduction in cross-section.
It will not so easy if the billet and the extruded component have a different profile, another means will be needed to relate their sizes. To relate this we use the term ‘extrusion ratio’ which is the ratio of the cross-sectional area of the billet (Ao) to the cross-section of the component after extrusion (Af)
To relate the cross section of the work piece to that of the extruded product, the extrusion ratio was established. The extrusion ratio is the ratio of the area of the work’s cross section (Ao) to that of the extrusion’s cross section (Af). The extrusion ratio, or reduction ratio, can be expressed as (Ao/Af).
The extrusion ratio will constantly be more than 1. It is possible to have extrusion ratios typically range from about 4 to 100 or even higher in certain special cases.
Shape Factor
The Shape of the required cross-section determines the force required to extrude the work. For example, simple round extruded part required lesser amount of force required to push the billet through die whereas complex shape like Aluminum profile requires more force. In order to term the required force in relation to the complexity of the shape, we use the ‘Shape Factor’.
The Shape factor is the ratio between the perimeter of the component cross section and the perimeter of a circle of diameter that extruded cross section can fit. A simple round profile has a shape factor of 1 and it increases as the cross-section becomes complex. The shape factor is lower means the relative force required to extrude that cross section is low.
You may have question of what about the work material? Whether it’ll affect force required to push the material?
You’re right! Though cross-section or profile of the extruded part is a large factor in calculation of force required in extrusion manufacturing operation, work material also important factor in determining the limitations for an extruded part. Stronger materials require more force to extrude, which limit the maximum size to be lower in case we need complex shape.
Extrusion Die
Metal extrusion die is the component that shape the forming metal and which are constant contact with the work material. So obviously we expect Extrusion die to be hard and strong, to maintain dimensional accuracy throughout the extrusion process when ram pushes billet material through it. Good wear resistance (So much of expectationJ) which is critical when manufacturing in large quantities. Extrusion dies used during hot extrusion should have good high thermal resistance and shouldn’t undergo granular changes at elevated temperatures.
To please us with all these requirement, Carbides and Tool Steel are most preferred material for metal extrusion dies.




























Discussion about this post