The Selection of Washers, Bolts, Nuts, etc. for a design should be a piece of cake compared to other components design. Just kidding you. It may be simple according to the observer but in real-time, it can be quite a tedious and important task. Engineers should consider a lot of careful consideration like temperature, corrosion, vibration, fatigue, initial preload, etc. before selecting any fasteners.
In this blog, we will give a proper introduction to Washers, type of Washers, selection and interesting application of Washers.
Washers
Washers are the disk-shaped thin plate with a hole in the middle (typically size of the Washer inner diameter is clearance value of the fastener it’ll be used along with). It is available either in metal or plastic depending upon the application.
What is a washer used for?
Do you know why Boeing 737 caught fire and exploded at the gate after landing at Naha in Okinawa, Japan? It is because somebody forgot to use a Washer where it was required.
Our humble-looking Washers have many purposes in the mechanical world. The main purposes are,
- Without the Washers, Screws or Bolts can damage the surface of the mating part while tightening. This damage will be leading to crack formation and an increasing probability of corrosion occurrence.
- When the mating part and fasteners material is different, it’ll lead to the corrosion problem. For example, if Steel Screw is used to secure the aluminum part without insulation of washers it’ll cause galvanic corrosion.
- The tightening force of the fastener is good enough to actually pull it straight through the material especially on soft material. A washer, in this case, allows the force to distribute local pressure around the Screw or Bolt location.
- Have you ever dealt with screw getting struck? This is because when Screw head sits on an uneven surface, it’ll end up tighter than it is supposed to.
- In machines, Vibration is unavoidable. As we read about the Boeing accident preventing the Screws from loosening is very important. To help with this, We have special purpose designed washers like Nord-Lock washers, Lock Washers, Spring Washers, etc. This special type of Washers will avoid Screws or Nuts from coming loose.
- Washers will play a role that is a combination of the above usages. You must have seen a lock washer used along with a larger diameter flat washer. This is to have multiple advantages.
Washers Standards – ANSI and BS
According to British Standards, Metric Series Metal Washers (BS4320), flat washers are specified as ‘Form’ which goes from Form A to G. This specification related to the outside diameter and thickness of the flat washers.
| Form A | Normal diameter and normal thickness |
| Form B | Normal diameter and light thickness |
| Form C | Large diameter and normal thickness |
| Form D | Large diameter and light thickness |
| Form E | Larger diameter and normal thickness |
| Form F | Larger diameter and normal thickness |
According to The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standards of Washers are specified as ‘Type’. Two types of flat washers are defined for general use.
Type A is a series of steel washers with broad tolerances, where design refinement is not important. They range from No. 6 to 3-in. hole size and from 3/16 to 5½-in. OD.
Type A washers are satisfactory for most assemblies. Type B washers are of higher quality and are specified in Narrow, Regular, and Wide diameters for each screw size from No. 0 to 3 in. However, many other standard sizes are available.
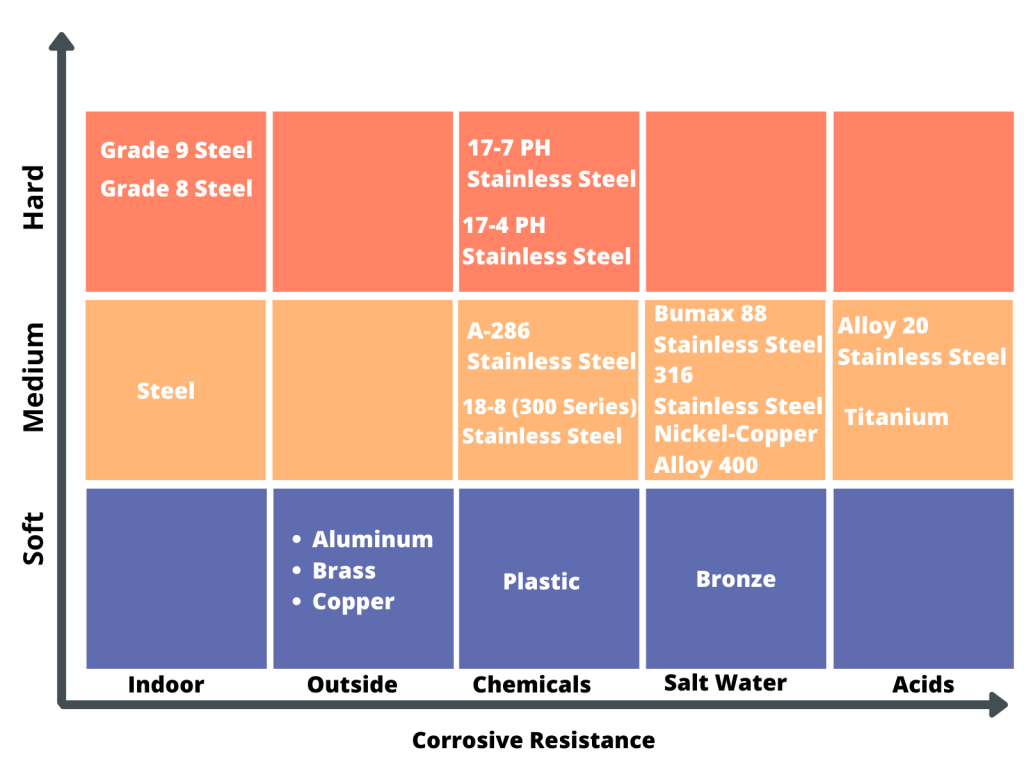
Washer Materials and Applications
In this section, I’ll go through different materials that washers come in.
- Brass – It is used in many common applications specifically in Plumbing ( hot water application).
- Silicon Bronze – It is mostly used in saltwater applications where we really don’t want any type of corrosion at all. Like in Boats and things of that nature.
- Stainless Steel – This is the most widely used material in washers. This is commonly used in a salty environment like saltwater, chlorine, coastal areas, and frequently salted roads. 304 SS is used in case freshwater applications. 18-8 stainless steel washers have good chemical resistance and mild magnetic.
- Plain Alloy – This is the structural flat washer used with structural bolts. This comes usually without coating so if it is exposed to the elements, it will rust and you’ll see pitting over time.
- Zinc Coated – Standard alloy steel coated with zinc. This can be used outside. You’ll see rust over time. But they will rust slowly. This won’t rust for at least 10 years though it depends on the environment. You’ll see the pitting along with the rusting on the edges. You’ll see this usage in many highway applications like guard tails, lamp post etc.to save money because it is cheaper than stainless steel
- Aluminum – It is ideal for outdoor use. It’s nonmagnetic.
What are the different types of washers?
Flat washers
Flat washers, is the most commonly used general-purpose washer (also called Type A plain washers). These washers are circular, thin, and flat with a hole (screw clearance) at the center. The plain washer is designed to spread the load from the screw and nut to a wide area. The plain washer also helps in case the hole is larger than the nut.
When to Use – By providing a wide bearing surface area, they distribute the load. Also in case our hole is oversized than the nut, we can use flat washers.
C-washers
C-Washes are also called Easy-Install Slotted Washers. C-washers have a slotted cut from the sides to the center. This slotted cut is the same width as the clearance hole (center hole) allowing the washer for quick install, remove without completely disassembling the screws.
When to Use – If the washer needs to be removed or replaced frequently, we can consider using C-washers. We can easily slide this in and out by just loosening the screw.
Shoulder washers
A shoulder washer also known as an insulation sleeve is designed to insulate screws, rivets or wire from an assembly. They look like a normal flat washer with a cylindrical sleeve attached to one side.
When to Use – Consider shoulder washer when you need to separate screws from the mating surface for various reason like heat flow, electrical insulation etc

D-shape washers or Clipped washer
D-shape washers refer to a flat edge cutaway on an outside diameter (perimeter). They are designed to prevent the washer from turning and loose by assembling the washer with a flat edge on its outside surface to align with a flat surface. This arrest rotational degree of freedom.
When to Use – Consider this washer when you face space limitation to around the washer or when you keep washer stationery. This is used in automotive, marine, aerospace, medical, etc.
Countersunk washers
Countersunk washers need to be used with countersunk screws. This washer keeps screw head in flush without the countersunk hole. As this washer provides a kind of finishing look to the assembly, it is normally called a finishing washer.
When to Use – When you need a flush surface without screw head protruding out.
Fender washers
Fender washers are similar to the flat washer but with a large outside diameter and regular inside diameter. They were initially used to mount fenders in the automobile as its large surface area distributes the load to even wide surface area as compared to the normal flat washer (also cheap).
When to Use – Commonly used in thin metal components. They find its application mostly in automobiles, paneling, and plumbing.
Torque washers
Screws and Bolts used in wood (soft materials) tend to lose its grip when wood material undergoes variable load, temperature. Torque washers are designed to have teeth that penetrate and anchor the bolt in place to the wood and other soft material to prevent rotation.
When to Use – Torque washer is ideal for uses in your woodworking projects when bolts need to not move around. But careful it is effective only in soft material. In the case of hard material, it can’t penetrate the surface.
Lock washers
Due to various reasons like vibration, material, etc fasteners have a tendency to rotate and disassemble from the assembly. This can be disastrous.
What is the purpose of lock washers?
Lock washers are designed to secure fasteners against the loosening of fasteners prone to rotation or the loss of friction. There are different types of lock washers available in the market and but all work under the same principle. They exert a continuous load by partially deforming, and secure a fastener in place.
Helical or Split Lock Washer
Helical Lock Washer is a non-continuous circular washer with its designed to bend outwards opposite to each other. As a screw is tightened, these washers flatten to add tension to the bolt head against the mating surface to prevent loosening from the thread.

Are split washers effective?
There are many studies that prove split lock washer ineffective as we originally claimed to prevent loosening. The body of evidence, based upon both experience and experimental results, is that they do not prevent loosening and can be shown to actually speed up the rate of loosening in many cases.
Even Nasa had said about the split lock washer. In NASA Reference Publication 1228 (1990) “Fastener Design Manual” addressed this issue as below,
“The typical helical spring washer … serves as a spring while the bolt is being tightened. However, the washer is normally flat by the time the bolt is fully torqued. At this time it is equivalent to a solid flat washer, and its locking ability is nonexistent. In summary, a lock washer of this type is useless for locking”
External tooth lock washers
External tooth lock washers have little prongs along the outside diameter and cylindrical inner diameter. If you look at them closely, those little prongs are a bit bent.When we put nut on it and tighten, nut gets locked on those prongs.
When to use – In case you need to lock a wide-headed nut or bolt head like round or pan head, consider external tooth washers.
Internal tooth lock washers
Internal tooth lock washers have their little prongs on the inside diameter and nice cylindrical outside surface.
When to use – Internal tooth lock washers work well with screws with smaller heads, like fillister head machine screws.
Spring washers
Spring washers, also known as disc springs, are metal discs made into an irregular shape to subject the washer to compress under the load pretty much like compression spring. This design provides a preload between joining surfaces.
This simple but brilliant design made this washer to be used in conditions where we need to compensate the movement in assembly, to act like a shock absorber under dynamic conditions.
Belleville washers
This is more a spring than a washer. Due to its springs characteristics, Belleville washers can accommodate more load with little deflection. We can increase its load carrying capacity by stacking during assembly.
If you find it difficult to pronounce it you can call this as Conical Spring Washer, Disc Spring Washer, Belleville Spring Washer or Cupped Spring Washer. I feel you man !

Wave washers
Wave washers offer moderate load capacity and deflection with its wave-like shape. They are commonly used as cushions or spacers.






























Discussion about this post