What is Hydrogen?
First element of the periodic table. Under normal conditions it is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas, composed of diatomic molecules, H 2 . The hydrogen atom, symbol H, consists of a nucleus with a positive charge unit and a single electron. It has atomic number 1 and an atomic weight of 1.00797.
What is Hydrogen made up of?
Hydrogen is a constituent of a very large number of compounds that contain one or more other elements. Those compounds include water, acids, bases, most organic compounds, and many minerals. Compounds in which hydrogen combines with only one other element are generally called hydrides.
It is one of the main constituents of water and all organic matter, and is widely distributed not only on Earth but throughout the universe. There are 3 isotopes of hydrogen: protium, of mass 1, which is found in more than 99.98% of the natural element; deuterium, of mass 2, which is approximately 0.02% in nature, and tritium, of mass 3, which occurs in small amounts in nature, but can be produced artificially through various nuclear reactions.
History of Hydrogen
The diatomic hydrogen gas, H 2 , was first artificially produced and formally described by T. von Hohenheim (aka Paracel ), which artificially obtained by mixing metals with acids strong. Paracelsus was unaware that the flammable gas generated in these chemical reactions was made up of a new chemical element .
In 1671 , Robert Boyle rediscovered and described the reaction between iron filings and dilute acids, resulting in the production of hydrogen gas. In 1766 ,Henry Cavendish was the first to recognize hydrogen gas as a discrete substance, identifying the gas produced in the metal-acid reaction as “flammable air” and discovering more deeply, in 1781, that the gas produces water when burned. Generally, it is given credit for its discovery as a chemical element. In 1783 , Antoine Lavoisier gave the element name hydrogen.
Properties of Hydrogen
Common hydrogen has a molecular weight of 2.01594. The gas has a density of 0.071 g/l at 0ºC and 1 atm. Its relative density, compared to that of air, is 0.0695. Hydrogen is the most flammable substance of all known. Hydrogen is slightly more soluble in organic solvents than it is in water. Many metals absorb hydrogen. Hydrogen adsorption on steel can make it brittle, leading to chemical process equipment failure.
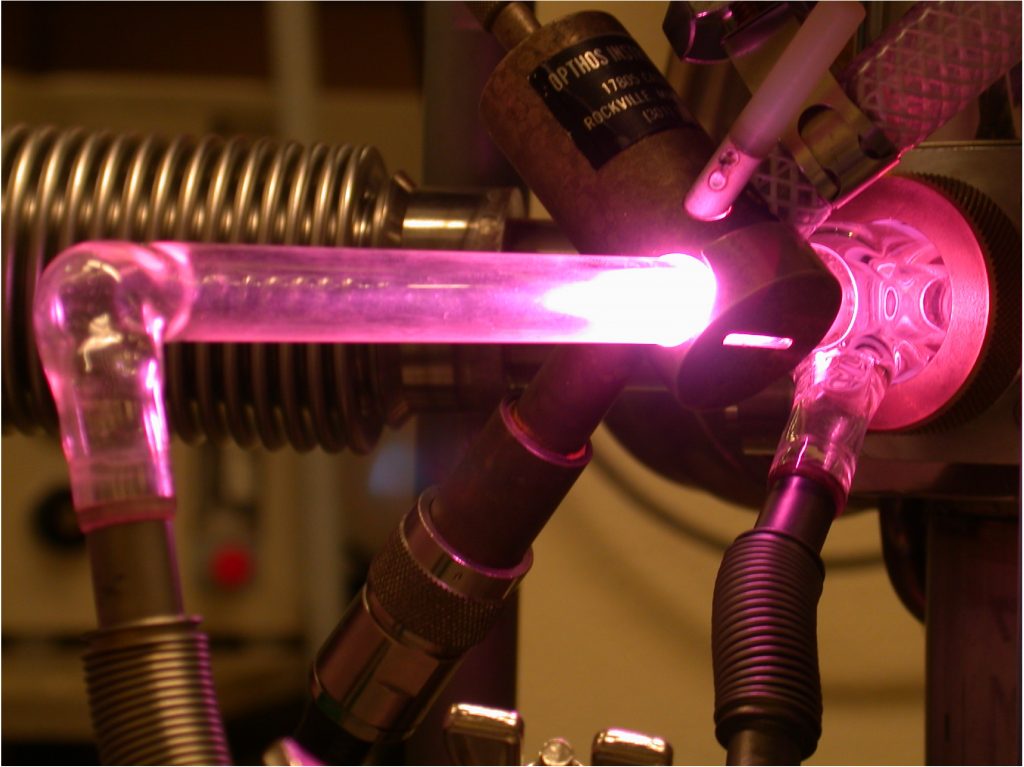
Chemical Reaction
Although generally diatomic, molecular hydrogen dissociates into free atoms at elevated temperatures. Atomic hydrogen is a powerful reducing agent, even at room temperature. It reacts with the oxides and chlorides of many metals, including silver, copper, lead, bismuth, and mercury, to produce free metals.
| Element Category | Reactive Nonmetal | Density | 0.08988 g/L |
| Block | S-block | Boiling Point | 20.271 K (−252.879 °C, −423.182 °F) |
| Atomic Number | 1 | Melting Point | 13.99 K (-259.16 °C, −434.49 °F) |
| Group | 1: H and alkali metals | Vaporization Heat | 0.904 kJ/mol |
| Period | period 1 | Fusion Heat | 0.117 kJ/mol |
| Electron Configuration | 1s1 | Molar Heat Capacity | 28.836 J/(mol·K) |
| Electrons per shell | 1 | Thermal Conductivity | 0.1805 W/(m·K) |
| Triple point | 13.8033 K, 7.041 kPa | Crystal Structure | hexagonal |
| Critical point | 32.938 K, 1.2858 MPa | CAS Number | 12385-13-6 1333-74-0 |
| Oxidation states | −1, +1 (an amphoteric oxide) | Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 2.20 |
| Ionization Energies | 1st: 1312.0 kJ/mol | Covalent Radius | 31±5 pm |
| Van der Waals radius | 120 pm | Natural Occurrence | primordial |
| Speed of sound | 1310 m/s (gas, 27 °C) | Atomic Weight | [1.00784, 1.00811] conventional: 1.008 |
It reduces to its metallic state some salts, such as nitrates, nitrites and sodium and potassium cyanides. Atomic hydrogen produces hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, with oxygen. With organic compounds, atomic hydrogen reacts to generate a complex mixture of products; with ethylene, C2H4 , for example, the products are ethane, C2H6 , and butane, C4H10 .
It reacts with a number of elements, both metals and non-metals, to produce hydrides, such as NaH, KH, H2S and PH3 . The heat that is released when the hydrogen atoms recombine to form the hydrogen molecules is used to obtain very high temperatures in atomic hydrogen welding.
Hydrogen reacts with oxygen to form water, and this reaction is extremely slow at room temperature; But if it is accelerated by a catalyst, such as platinum, or an electrical spark, it is done with explosive violence. With nitrogen, hydrogen undergoes an important reaction to give ammonia. Hydrogen reacts at elevated temperatures with a number of metals and produces hydrides. The oxides of many metals are reduced by hydrogen at elevated temperatures to obtain the free metal or a lower oxide. Hydrogen reacts at room temperature with salts of less electropositive metals and reduces them to their metallic state. In the presence of a suitable catalyst, hydrogen reacts with unsaturated organic compounds by adding to the double bond.
What is hydrogen used for?
- Oil Refineries Hydrogen has the highest energy content by weight of any chemical fuel – three times higher than gasoline and it is critical feedstock for the chemical industry including oil refining. Hydrogen utilization is increasing rapidly in petroleum refining operations, such as hydrocracking, and in to remove sulfur by treating with Hydrogen .
- Energy Industry It also powers fue cells with little or no emissions. Advances in hydrogen technology could spur innovation in everything from steel manufacturing and iron production to energy storage and transportation by light-duty and heavy-duty vehicles, trains, planes and boats.
- Fertilizer ProductionThe most important use of hydrogen is in the synthesis of ammonia.
- Chemical Industry Large amounts of hydrogen are consumed in the catalytic hydrogenation of unsaturated liquid vegetable oils to obtain solid fats. Hydrogenation is used in the manufacture of organic chemicals.
- Rocket Fuel Large quantities of hydrogen are used as rocket fuel, in combination with oxygen or fluorine, and as a propellant for nuclear powered rocket.
How is Hydrogen produced?
A wide variety of methods can be applied to prepare hydrogen gas. The choice of method depends on factors such as the amount of hydrogen desired, the required purity, and the availability and cost of the raw material. Among the processes most used are the reactions of metals with water or acids, the electrolysis of water, the reaction of steam with hydrocarbons or other organic materials, and the thermal decomposition of hydrocarbons. The main feedstock for hydrogen production are hydrocarbons, such as natural gas, refined oil gas, gasoline, fuel oil, and crude oil.
Effects of Hydrogen on health
Effects of hydrogen exposure:
Individuals who breathe this atmosphere may experience symptoms including headaches, ringing in the ears, dizziness, drowsiness, unconsciousness, nausea, vomiting, and depression of all the senses. The skin of a victim may be blue. Under some circumstances, death can occur. It is not expected to cause mutagenesis, embryo toxicity, teratogenicity, or reproductive toxicity. Pre-existing respiratory diseases can be aggravated by overexposure to it. Measure hydrogen concentrations with a suitable gas detector (a normally flammable gas detector is not suitable for this purpose).

Physical hazards :
Gas mixes well with air, explosive mixtures are easily formed. Gas is lighter than air. At ordinary temperatures hydrogen is a poorly reactive substance unless it has been activated in some way; for example, by a suitable catalyst. At elevated temperatures it is very reactive.
Chemical Hazards:
Heating can cause violent combustion or explosion. Reacts violently with air, oxygen, halogens, and strong oxidants causing fire and explosion hazard. Metallic catalysts, such as platinum and nickel, greatly enhance these reactions.































Discussion about this post