What is Parallelism GD&T?
Parallelism controls the surface, midplane or axis which need to be in parallel or 180deg with respect the datum surface. It is just the extension of angularity tolerance with specific control on angle of orientation. In this case it is 180 deg. So Angularity symbol may be interchangeably used in place of Parallelism and Perpendicularity.
What is Parallelism in Drawing?
The shape of the tolerance zone for parallelism is 2 parallel planes with thickness as mentioned in tolerance value. In below example, all the elements of the surface must lie within this tolerance zone.
Note that tolerance zone location is controlled by basic dimension, plus/minus or limits of the size or profile tolerance on this part. To have effective control of parallelism between two planes, the tolerance should be tighter. If you are using parallelism along with the profile tolerance control, then make sure that parallelism tolerance should be tighter than profile.
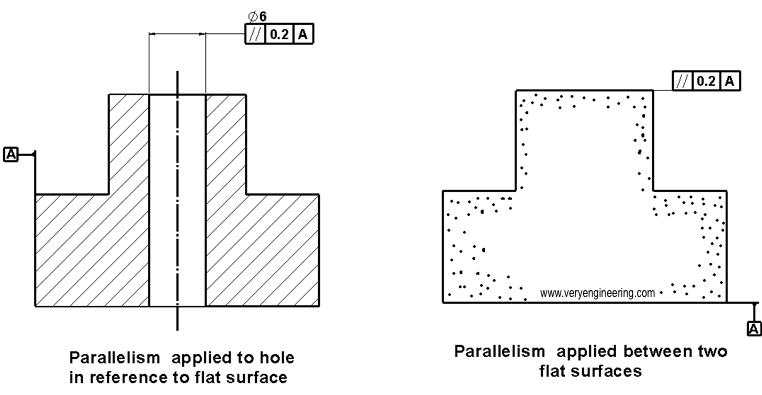
How to Apply Parallelism GD&T?
Identify the surface: As per your design requirement first identify your surfaces which need to be parallel to each other. This can be external planar surface, axis of the holes or midplane of the two face.
Set the reference Plane or Datum: Parallelism is measured with relative to another surface or axis. So we need a flat surface which will be used as the datum. In our drawing it’ll be denoted with Letter enveloped by the square box.
Set the tolerance value: At this point, you’ll define how tight you want that surface to be in parallel to the datum. Your requirement can be 0.2mm or 0.002mm.
How is Parallelism Tolerance Measured?
There are several methods to measure parallelism. The most common method is by measuring parallel with reference to surface plate. In this method, Component is placed on the flat base. Ensure that datum surface is must be clean and accurate depends upon the level of precision you want.
Then the dial indicator is moved across the surface. Indicator must fall within the tolerance level otherwise component is failed for Parallelism.
Make sure that your measurement is taken at consistent room temperature in case of very tight tolerance requirement. Even the little variation in temperature will affect the value as some material tends to expand or contract as the temperature changes.
Parallelism Application
Parallelism is applied when two parts or two faces need to be in parallel to each other to achieve design intentions.
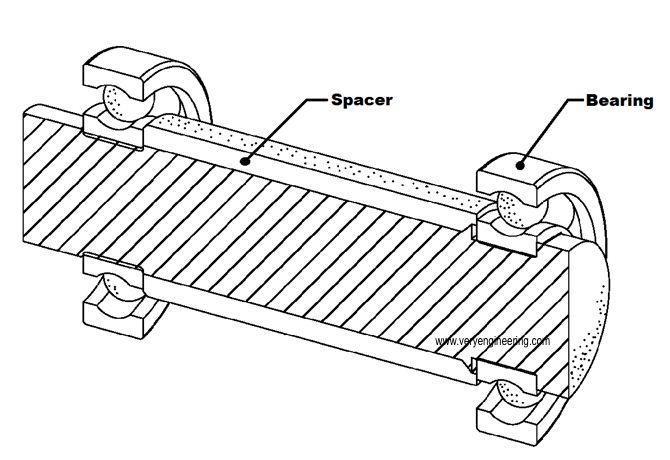
It is not necessary to have parallelism between two surfaces but also can be between two holes or hole and flat faces. Below example explains how parallelism controls the critical function between two bearings. Here, it is critical to have two bearings to be in parallel to each other. To achieve this, spacer component between the two bearings is applied with parallelism.






























Discussion about this post